Table of Contents
What Is Nanotechnology?
Introduction: The Nano Revolution Begins
The world is entering the brand new era – Nano Revolution, a time when science hereto is at the scale of a millionths less than the diameter of a human hair. What Is Nanotechnology is about the materials and devices that are made at the atomic and molecular scale which result in innovations that were never considered before.
Nanoscience has revolutionized all facets of human life due to more robust machinery and improved electronics, precise drug delivery, and renewal energy. Well, guess what, clothes that never are washed, medicines that locate and kill cancer cells, and solar panels that nearly collect and use all of the sunlight — all of this happened through What Is Nanotechnology.
It is not only a revolution on small matters but on smart, efficient, smart and sustainable matters. With scientists trying to unravel this world of invisibility, What Is Nanotechnology promises to define the future of health care and the work environment, and communication and daily living. The nano revolution really is the giant leap in human development and it is the way of defining anew how we perceive the matter itself and how we use it.
Historical Evolution of Nanoscience

Development of Nanoscience: From Concept to Fabrication
Nanotechnology has a span of decades, starting with conceptual prediction and growing into practical tools and applications. While many link this new area of science to a famous lecture, the full historical context includes the works of two more influential figures, Norio Taniguchi and Eric Drexler.
The Conceptual Seed (1959): Richard Feynman
The conceptual basis of what is nanotechnology is commonly considered to be physicist Richard Feynman. In his famous 1959 talk, entitled “There’s Plenty of Room at the Bottom”, Feynman presented the notion of controlling matter on scales that enable the control of individual atoms and molecules. It was a theoretical provocation to present the possibilities of ultra-miniaturization long before the tools to implement it had been invented.
The Termite (1974): Norio Taniguchi
The notion of what is nanotechnology as a defined term further evolved with its introduction, much later, in 1974 by Japanese scientist Norio Taniguchi of the Tokyo University of Science.
Taniguchi used this terminology to refer to a paper focused on the order of required precision to machine materials with tolerances finer than a micrometer, and in fact specified a range of dimensions in the nanometer range (one billionth of a meter).
Molecular Assemblers Vision (1980s): Eric Drexler.
The contemporary, futuristic idea of what is nanotechnology is called Molecular Nanotechnology (MNT) brought into most modern popularity by American engineer Eric Drexler.
In the late 1980s, Drexler published the book Engines of Creation: The Coming Era of Nanotechnology. In that book Drexler proposed the idea of molecular assemblers and nanobots: tiny machines (and replicators) that are able to position management of individual atoms and molecules, and build complex structures.
Drexler was able to shift the focus from precision engineering to bottom-up construction. He envisioned a world in the future where everything could be built up from the bottom small things to the larger: all things could be made from the bottom up atom by atom. Drexler’s theoretical schema has provided inspiration for the following generations of nanoscientists and researchers.
This arc of progression—from Feynman’s theoretical idea, to Taniguchi’s technical term, to Drexler’s radical molecular vision—gives us a complete historical context of what is nanotechnology and the progress of nanoscience into the idea of what nanoscience means today.
Understanding the Nanoscale: Principles and Dimensions
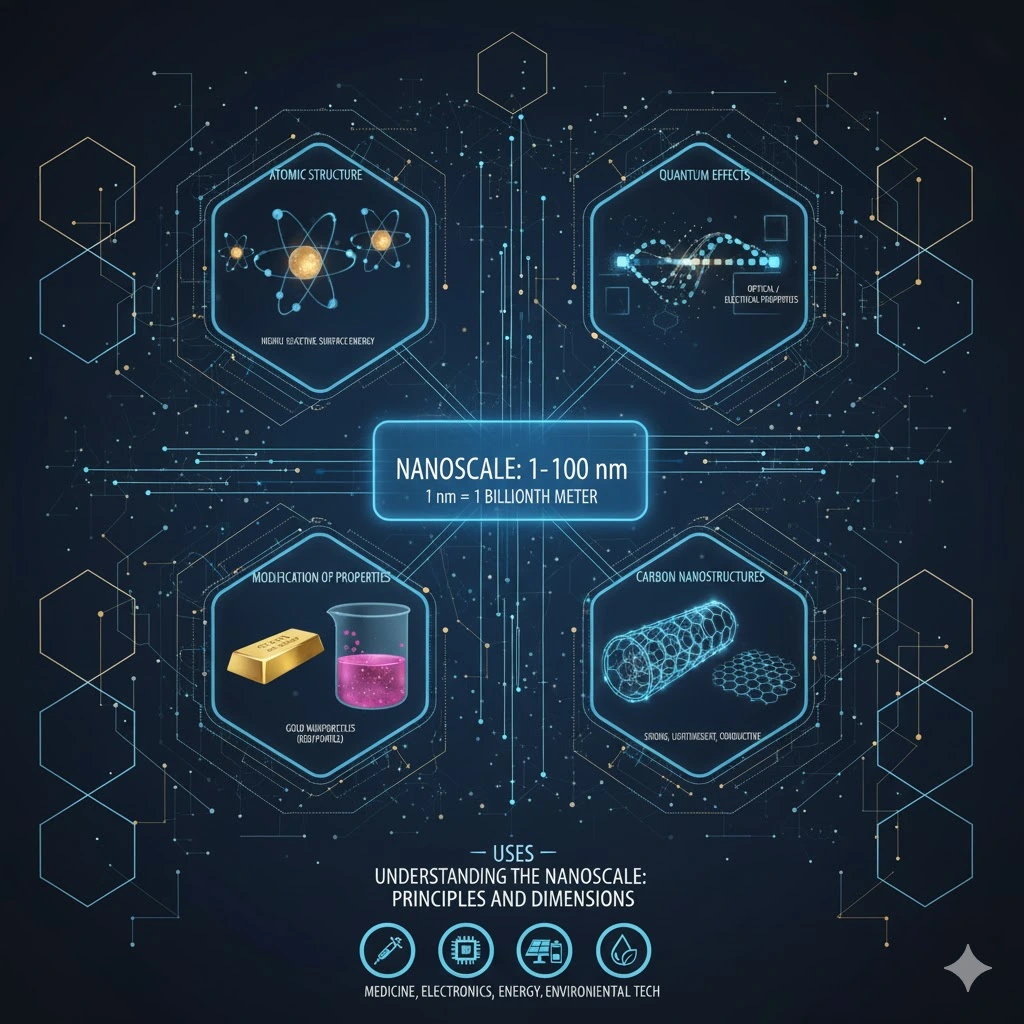
Nanoscale: principles and dimensions biology of the nanoscale Systems at the nanoscale Interfaces at the nanoscale
Definition Nanoscale means 1-100nm; 1nm=1 billionth meter.
- Atomic Structure : The structure becomes highly reactive, and most of the atoms are found at the surface at this scale upon which energy is located on the surface.
- Quantum Effects : Because of their interactions, What Is Nanotechnology explains that the behaviour of electrons and photons is not the same but shows discrete values of electric charge and unique optical/electrical properties.
- Modification of Properties : Not only are What Is Nanotechnology materials different in color, strength, conductivity, and even melting point than the bulk materials (e.g., gold nanoparticles are red/purple).
- Carbon Nanostructures : Carbon constitutes nanotubes or graphene that are highly strong, light in weight and conductive.
Significance The behavior at nanoscale is imperative to the design of materials of improved mechanical, electrical or chemical characteristics.
Uses:EEVN: C AD® Playing a vital role in medicine (delivery of specific drugs, drugs), electronics (smaller, faster devices), energy (untinted solar panel, battery), and environmental technology (cleanwater purification, environmental pollution).
How Nanotechnology Works?

Nanotechnology works on very tiny particles which are smaller than a cell into structure . It only focuses on working at atomic and molecular level.
There are mainly Four important mechanisms that help it work:
- Self-Assembly : In this process, atoms or molecules are arranged automatically into an organized structure. It is like how puzzle pieces fit together on their own. What Is Nanotechnology uses self-assembly to build nanostructures, coatings.
- Molecular Manipulation : In this atoms or molecules are rearranged by using special tools such as the Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) or Atomic Force Microscope (AFM), scientists move or control single molecules to build new materials. It is like shaping things molecule by molecule.
- Bottom-Up Engineering : What Is Nanotechnology builds big structures from small particles, starting from the bottom level (atoms) and going up, instead of cutting large parts into smaller pieces of material.
| Method | Description | Example |
| Self-Assembly | Molecules spontaneously organize into structures using forces like hydrogen bonds. | Creating DNA origami or lipid bilayers. |
| Molecular Manipulation | Using tools (like AFM/STM tips) to directly move individual atoms into specific positions. | ‘Writing’ patterns on a surface atom-by-atom. |
4. Top-Down Fabrication (Destructive)
This method starts with larger materials and uses high-precision tools to cut, etch, or carve them down to nanoscale sizes (miniaturization) which is the key What Is Nanotechnology
| Method | Description | Example |
| Photolithography | Using light to transfer patterns onto a substrate (used heavily in electronics). | Manufacturing modern integrated circuits (microchips). |
| Etching/Milling | Chemically or physically removing material according to the defined pattern. | Creating micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS). |
Top-Down vs. Bottom-Up: The Two Main Approaches
| Feature | Bottom-Up | Top-Down |
| Starting Point | Atoms/Molecules | Bulk Materials |
| Action | Adding Material (Construction) | Removing Material (Miniaturization) |
Nanomaterials and Nanoparticles: Similarities and Differences
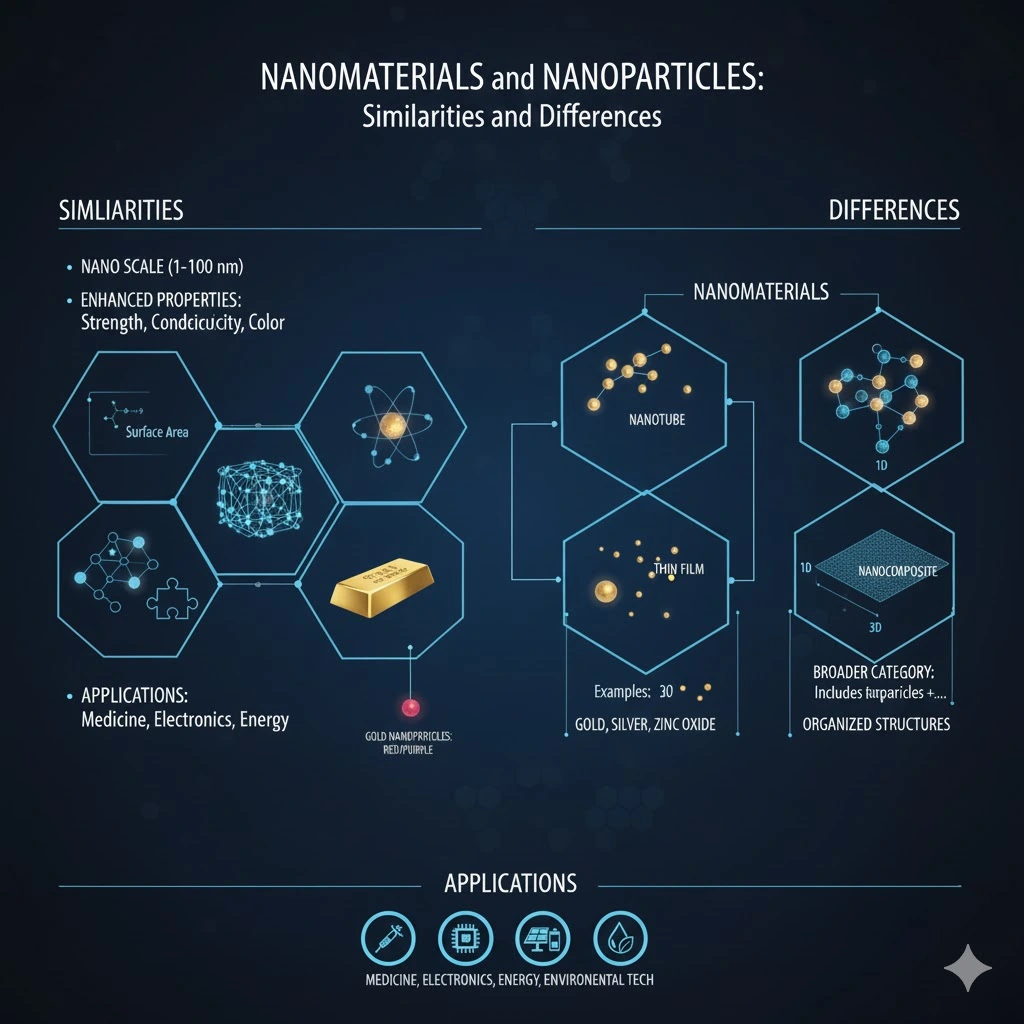
Nanoparticles and Nanomaterials: Empirical Comparisons and differences. Nanoparticles and nanomaterials: Dissimilarities and parallels.
Introduction
What Is Nanotechnology involves nanomaterials and nanoparticles that are devised and researched on a grand scale at nanosizes (1–100 nanometers), which are a few thousand nanoparticles wide over the length of a human hair. This is the scale where matter behaves differently due to two dominant reasons, large surface area and quantum effects. Such factors provide nanomaterials with special mechanical, optical, and electrical properties.
Similarities
- They are both in the realm of the nano.
- Both are stronger, more reactive, conductive, as well as have changed color to better than bulk materials.
- Applied in other related areas – medicine, electronics, energy, environment and textiles.
- They are highly reliant on size, shape and surface properties.
Differences
- A nanoparticles consists of single, small particles typically in the form of a sphere or other irregular irregular shapes and therefore is termed as 0-dimensional (0D), as all dimensions are smaller than 100nm. Sample: gold, silver, and zinc oxide nanoparticles.
- Nanomaterials is a fringe category – it contains nanoparticles, as well as nanotube (1D), thin films (2D), and nanocomposites (3D).
- Nanomaterials are commonly structured or organized into networks although nanoparticles are small separate entities.
- Nanoparticles primarily concern surface reactions, but nanomaterials may actually possess bulk mechanical, or even electrical, action.
Structure and Behaviour
At the nanoscales, What Is Nanotechnology shows that the atoms on the surface supersede the other materials, making their reactivity and catalytic ability more active. Quantum confinement results in the varying color, melting point, magnetic, and optical characteristics of these materials. For example, gold nanoparticles do not show metallic yellow but are instead red or purple.
Development Applications and Significance.
- Medical : drug delivery, Agent targeting, imaging and use in treatment of cancer.
- Industrial : more resolute lightweight compounds, sensors, paints, batteries and solar cells.
- Environmental : pollution management, sewage purification and self cleaning products.
Types and Classifications of Nanomaterials
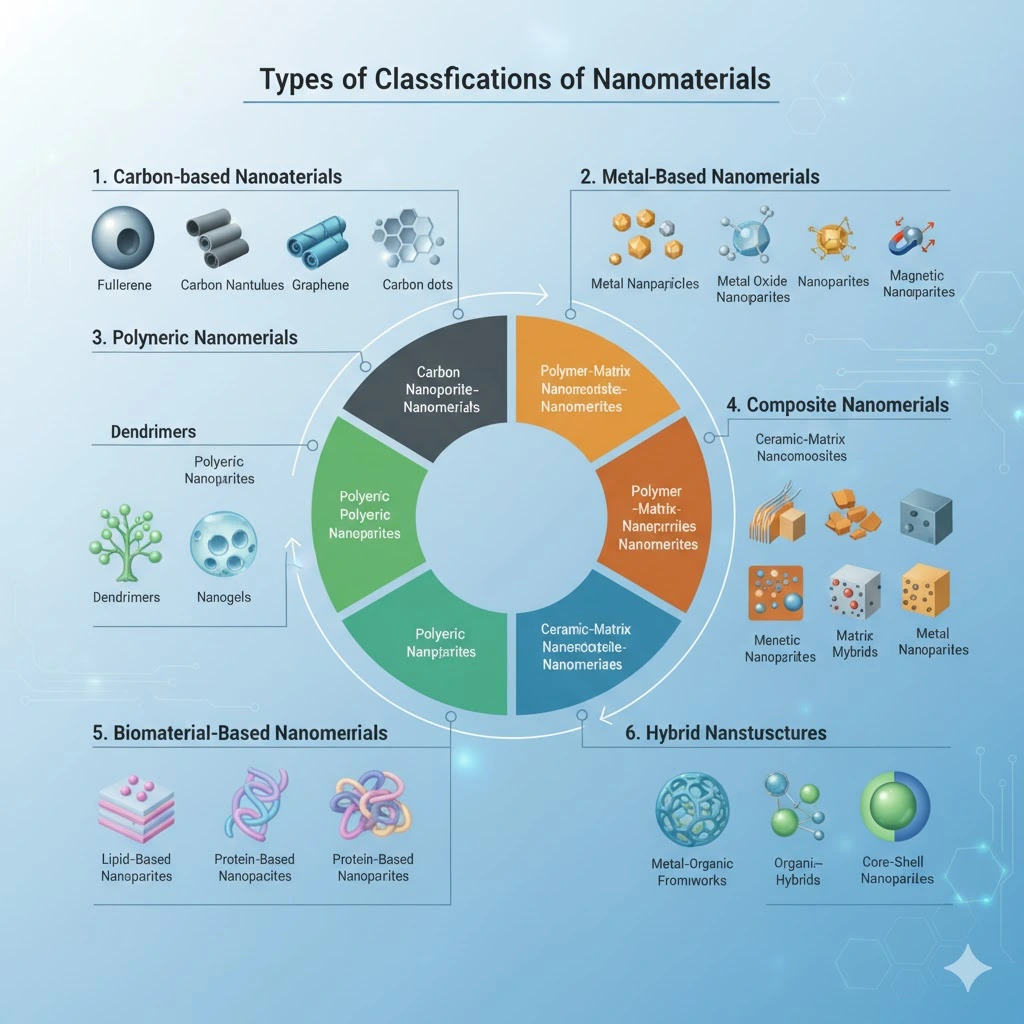
Following are the types and classification of Nanomaterials :-
1. Carbon – based Nanomaterials
Carbon-based What Is Nanotechnology materials are mainly made up of carbon atoms, which are organized into specific nanostructures and are highly studied for their excellent mechanical, electrical, and thermal characteristics.
SUBTYPES:
- Fullerenes- These What Is Nanotechnology molecules made up of carbon form hollow spheres, ellipsoids, or tubular structures. They have notable electron-accepting characteristics and are employed in drug delivery, solar cells, and lubricants.
- Carbon Nanotubes- Cylindrical structures consist of graphene sheets which are rolled into tubes.They have unique strength , excellent electrical conductivity and wide thermal stability.Properties include electronics, sensors and composite materials.
- Graphene- What Is Nanotechnology material made up of a single layer of carbon atoms in a 2D honeycomb structure. It has excellent electrical conductivity, transparency, and mechanical strength, and is used in supercapacitors, flexible electronics, and biomedical devices.
- Carbon dots- Nano sized carbon particles with glow properties. They are highly used in sensing , bioimaging and drug delivery systems.
2. Metal -Based Nanomaterials
These nanomaterials are made up of metals or metal oxides in nanoscale form .They show notable optical , magnetic and catalytic features.
SUBTYPES:
- Metal Nanoparticles- What Is Nanotechnology includes gold, silver, platinum, and palladium nanoparticles. They exhibit optical characteristics depending upon their size, for example, surface plasmon resonance, and are employed in catalysis, sensors, and biomedical fields.
- Metal Oxide Nanoparticles- This include titanium dioxide , zinc oxide and iron oxide . They have a wide surface reactivity which are applied in photocatalysis, environmental cleanup and magnetic resonance imaging.
- Magnetic Nanoparticles- What Is Nanotechnology includes iron, cobalt, and nickel-based materials. They are aligned with magnetic fields and are applied in data storage, targeted drug delivery, and magnetic hyperthermia therapies for cancer.
3. Polymeric Nanomaterials
What Is Nanotechnology includes nanomaterials which are composed of natural or synthetic polymers. They are employed in drug delivery, tissue engineering, and for nanocomposite materials.
SUBTYPES:
- Dendrimers- They are widely branched, tree-like polymers and have multiple functional groups. They can transport drugs, genes and imaging agents.
- Polymeric Nanoparticles- They are the solid polymer particles which are at the nanoscale for eg PLGA or PEG- based nanoparticles and used for controlling drug delivery and nanocarriers.
- Nanogels- What Is Nanotechnology involves hydrophilic polymer frameworks that are capable of absorbing water and encapsulating bioactive molecules. They are employed in targeted therapies and wound healing.
4. Composite Nanomaterial
Merge 2 or more various nanomaterials to obtain enhanced features. They often combine the strengths of each component.
SUBTYPES:
- Polymer – Matrix Nanocomposites- Polymers enhanced with nanoparticles such as CNTs, graphene and metal oxides to improve mechanical, thermal, or electrical features.
- Ceramic- Matrix Nanocomposites- Ceramics added with nanoparticles to enhance hardness, thermal stability and fracture toughness.
- Metal – Matrix Nanocomposites- Metals enhanced with nanoparticles to increase mechanical features and corrosion resistance.
5. Biomaterials- Based Nanomaterials
They are obtained from or suitable with biological systems. They are used in medical and pharmaceutical applications.
SUBTYPES:
- Lipid -Based Nanoparticles- This includes liposomes and solid lipid nanoparticles which are used in gene and drug delivery.
- Protein – Based Nanoparticles- Composed from albumin, gelatin and tissue engineering .
- DNA/ RNA Nanostructures- Self organized nanostructures which are used in gene therapy or molecular diagnostics.
6. Hybrid Nanostructures
Merge various types of nanomaterials to form multifunctional systems. They are created to harness the advantages of each part.
SUBTYPES:
- Metal Organic Frameworks- Porous structures made up of metal ions and organic molecules which are employed for gas storage, catalysis and drug delivery.
- Organic Inorganic Hybrids- What Is Nanotechnology includes nanomaterials that link inorganic nanoparticles with organic polymers and biomolecules for use in sensors, electronics, and biomedical fields.
- Core Shell Nanoparticles- Nanoparticles where one material made the core and another made the shell to regulate reactivity, stability and targeting fields.
Characterization tools and Analytical Methods in Nanotechnology
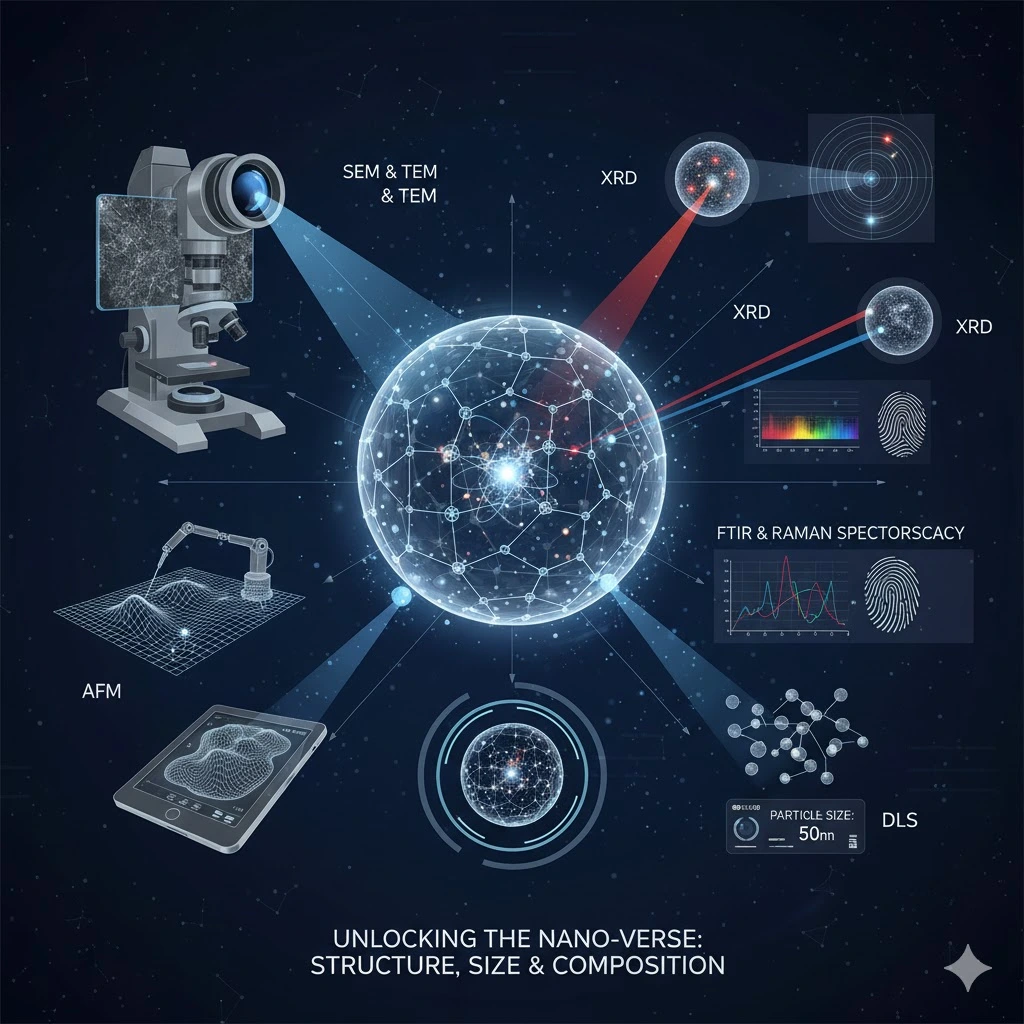
What Is Nanotechnology is about exploring the nanotechnology world, which is like opening a concealed universe invisible to the eyes. To understand how these tiny materials behave, we depend on smart tools and powerful techniques.
- SEM and TEM – These are ultra stong cameras and give high resolution images of surface and internal details structure of nanoparticles
- AFM – works like gently ‘feels’the surface and tracing every bump to create 3D image.
- XRD – helps in identification of how the atoms are arranged in crystals.
- FTIR & Raman Spectroscopy – reveal what molecules are made of by studying how they interact like absorbs or scatter light.
- DLS – Compute how particles move in liquid to estimate their size.
- XPS (X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy)
- The Analogy: If SEM/TEM is taking a photo of a person, XPS is checking their fingerprints and DNA.
- What it does: It shoots X-rays at the surface and measures the electrons that bounce off.
- Why it matters: It is incredibly surface-sensitive (only looks at the top 1–10 nm). It tells you not just what elements are there, but how they are bonded (e.g., is it pure Iron or Iron Oxide rust?).
- Zeta Potential Analysis
- The Analogy: The “Social Distancing” meter for nanoparticles.
- What it does: It measures the electric charge cloud surrounding a particle in liquid.
- Why it matters: If particles have a high Zeta Potential (high charge), they repel each other and stay floating (stable). If the charge is low, they crash into each other and clump up (flocculate). This is critical for making medicines that don’t separate in the bottle.
- BET Analysis (Brunauer-Emmett-Teller)
- The Analogy: Measuring the surface of a sponge.
- What it does: It releases gas (usually Nitrogen) onto the material and measures how much gas “sticks” to the surface.
- Why it matters: Nanomaterials are famous for having huge surface areas. BET calculates the exact surface area, which helps predict how well a material will work as a catalyst or a filter.
What Is Nanotechnology, when used together with these tools, paints a full picture of a material’s structure, size, and composition, and how it behaves. It allows researchers to design stronger and more efficient nanomaterials — knowledge that’s driving innovation in medicine, energy, and modern technology.
Applications of Nanotechnology in Real Life
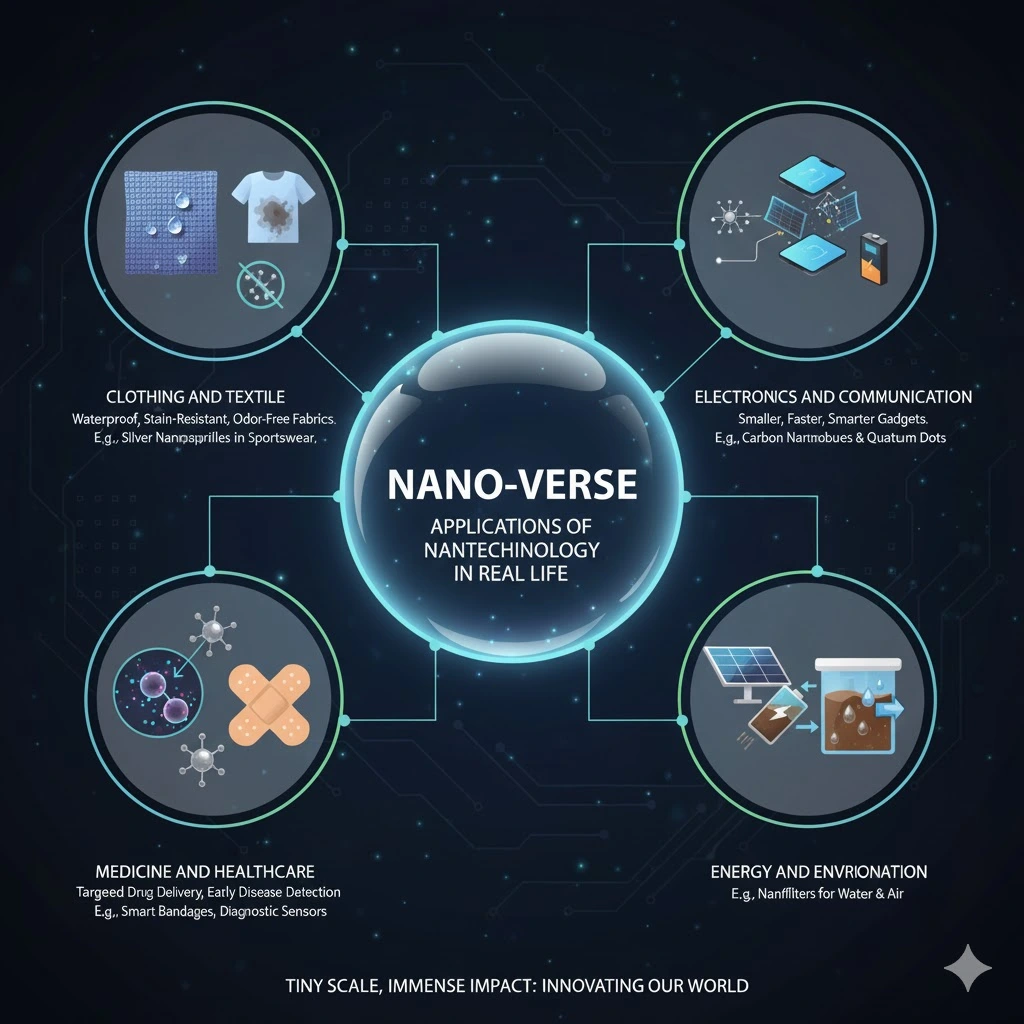
What Is Nanotechnology is about working with materials at a very small scale. Scientists deal with structures smaller than a human hair by about 80,000 times. When scientists work at this tiny level, materials show new and unique properties, and because of this microscopic work, we can enhance our everyday products, making them better, smaller, and more useful.
1- Clothing and Textile
What Is Nanotechnology is used in the clothing and textile industry to make better and more comfortable fabrics. Clothes can be made waterproof, stain-resistant, wrinkle-free, and odor-free.
For example- silver nanoparticles are added to sportswear cloth to stop bad smells caused by sweat.
2- Electronics and communication
What Is Nanotechnology has made our gadgets smaller, faster, and smarter than before. The chips inside our phones, laptops, and smartwatches are built using nanoscale materials. This helps them store more data, run at higher speeds, and use less power.
For example- Carbon nanotubes and quantum dots are examples of nanomaterials used to make better screens, batteries, and flexible displays.
3-Medicine and Healthcare
What Is Nanotechnology has one of its most powerful uses in medicine. Doctors now use nanoparticles to deliver medicines directly to the parts of the body that need them.
For example- Nanotechnology is used to make smart bandages to be aware about infections, tiny diagnostic sensors to detect diseases like cancer or diabetes at early stages.
4- Energy and Environment
What Is Nanotechnology plays a key role in producing clean energy. Solar panels made with nanomaterials can absorb more sunlight and convert it into electricity more efficiently. Even batteries with nanotech charge faster and last longer, helping to clean and sustain our environment.
For example- Nanofillers purify the water and remove harmful chemicals and bacteria from water. In factories, it helps to reduce air pollution by breaking down toxic gases. Nanotechnology plays an important role and steps toward a cleaner and greener future.
5. Agriculture and Food Technology
What Is Nanotechnology explains how Agri-Food Tech applies advanced technology across the entire food supply chain (farm to fork) to boost efficiency, sustainability, and food safety
For Example : Farmers use GPS, drones, and soil nano sensors to gather real-time data on their fields. This allows them to apply resources (like water, fertilizer, or pesticides) only to the specific spots that need them, dramatically reducing waste and increasing crop yield efficiency
Consumer Application: Cosmetics
Nanotechnology primarily improves sunscreens for a better user experience.
- Invisible Protection: By using nanoscale Zinc Oxide (ZnO) and Titanium Dioxide (TiO2), sunscreens block UV light effectively but remain transparent (no white residue).
- Other Benefits: Nano capsules also improve the delivery of active ingredients (vitamins) and enhance the stability of creams.
AI + Nanotechnology: The Smart Duo Shaping the Future
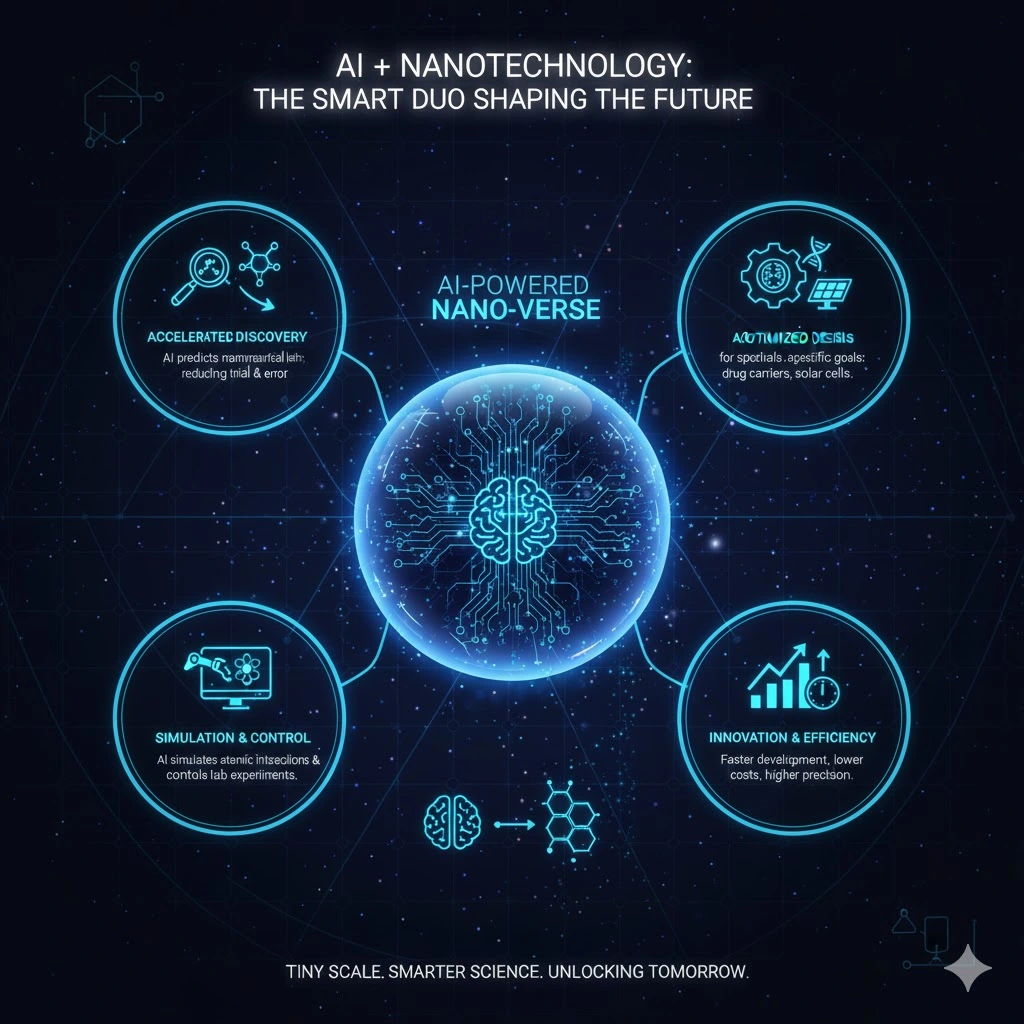
What Is Nanotechnology, combined with Artificial Intelligence (AI), is teaming up to change the game at the smallest scale. Previously, designing new nanomaterials required endless experiments, but AI is speeding up the process by predicting outcomes before they happen. Using machine learning models, scientists can analyze massive data sets of nanomaterial structures and properties to find patterns and predict how new combinations will behave.
What Is Nanotechnology works hand in hand with AI, which doesn’t just guess—it helps design materials for specific goals like stronger coatings, smarter drug carriers, or highly efficient solar cells. It can simulate atomic interactions, optimize synthesis conditions, and even control lab experiments through automated “self-driving” systems. This reduces trial and error, saving both time and money.
What Is Nanotechnology, when combined with Artificial Intelligence and nanoscience engineering, is helping researchers unlock breakthroughs in medicine, clean energy, and advanced electronics. The time and cost to develop new materials are reduced, while precision and innovation increase. The partnership between AI and nanotechnology is not just futuristic — it’s reshaping innovation today.
The collaboration between AI and nanotechnology goes far beyond simple predictions; it is creating entirely new ways to conduct science. Here is a deeper look at the specific mechanisms and revolutionary tools emerging from this partnership.
1. The “Inverse Design” Revolution
Traditionally, scientists mix ingredients and check the results to see if they got lucky. AI flips this process on its head.
- How it works: Researchers tell the AI the exact properties they need—for example, a material that is “transparent like glass but conductive like copper.”
- The AI’s Role: Using advanced algorithms (such as Generative Adversarial Networks or GANs), the AI works backward to generate the precise atomic structure required to achieve those properties.
- Real-World Impact: This technique is currently being used to design metasurfaces—flat, nanoscale optical chips that can replace bulky camera lenses in smartphones and medical sensors.
2. Self-Driving Laboratories
Imagine a lab that runs 24/7 without a single human inside. This is no longer science fiction; it is the reality of “Self-Driving Labs” (SDLs).
- Robotic Chemistry: In these labs, AI algorithms control robotic arms that pipette fluids, heat samples, and run microscopes.
- Closed-Loop Discovery: The AI analyzes the result of Experiment A and immediately decides what Experiment B should be to get a better result.
- Example: The Polybot at Argonne National Laboratory is an AI-driven robot that autonomously processes electronic polymers, testing hundreds of variations in a day—a task that would take a human researcher months.
3. AI as the Ultimate Lens
We use powerful tools like SEM and TEM to see nanoparticles, but these images are often noisy or difficult to interpret. AI acts as a digital enhancement layer for these microscopes.
- Instant Analysis: Instead of a human manually counting thousands of nanoparticles in an image to estimate their size (a process that takes hours), AI computer vision models can segment and measure them in seconds with higher accuracy.
- Super-Resolution: Deep learning models can take low-resolution electron microscope images and mathematically “fill in the blanks” to create sharper, clearer images, allowing scientists to see atomic defects that were previously invisible.
Global and Local Perspectives
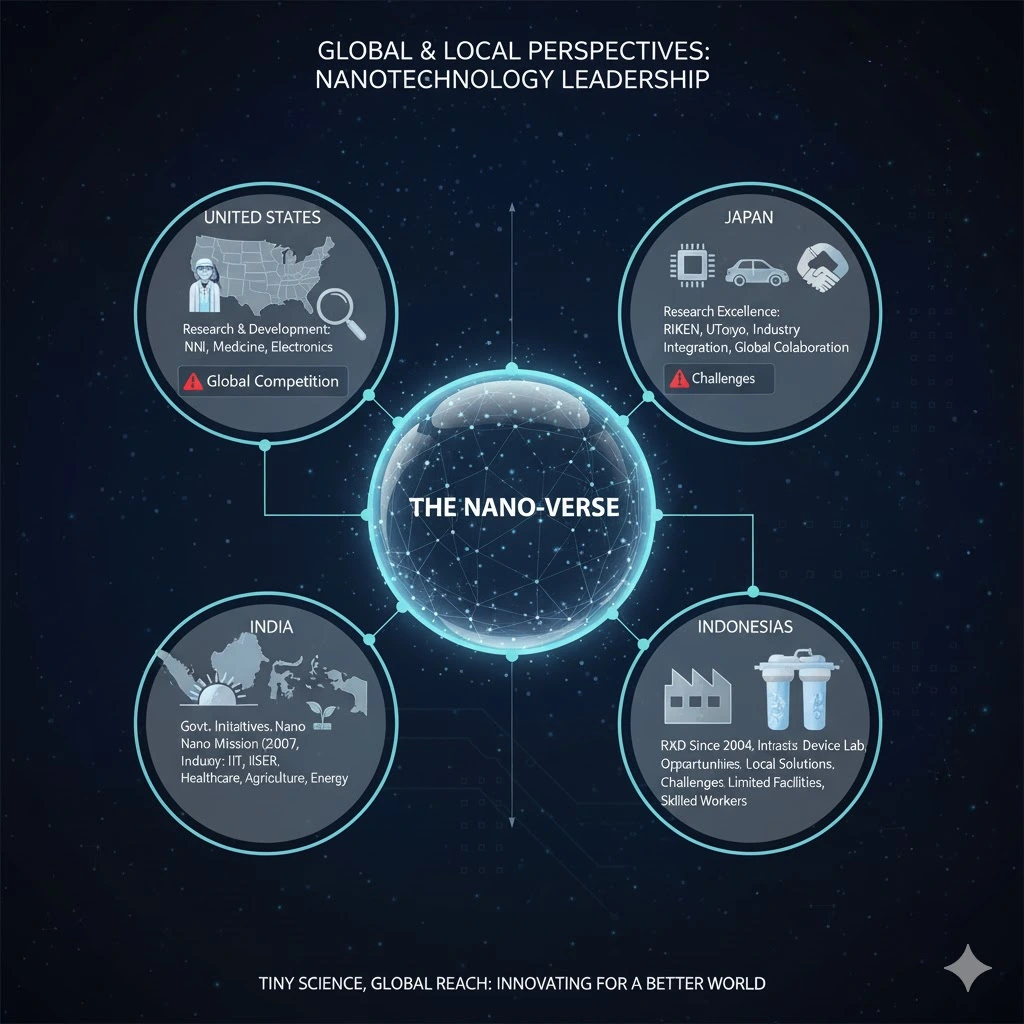
Global Perspective : Leading Nations in Nanotechnology
United States
- Research and Development – The U.S. remains a leader in this field of nanotechnology, supported by major investments in research and development. The National Nanotechnology Initiative (NNI) has played a vital role in coordinating federal actions. a clear example of how What Is Nanotechnology continues to drive innovation and global leadership.
- Applications – It is highly used in medicine, electronics and defense. Firms like ARIZ Precision Medicine are employed for drug delivery in cancer treatment.
- Challenges – Even the U.S. spends on research and development , they face struggles in keeping their dominance because of increasing global demand.
Japan
- Research excellence – Japan is well known for its developments in nanomaterials and advances in manufacturing. Institutions such as RIKEN and the University of Tokyo are leading in nanotechnology, showcasing how What Is Nanotechnology contributes to the nation’s progress in science and innovation.
- Industry integration – Japan’s industries efficiently used nanotechnology in electronics, automotive and healthcare fields.
- International Collaboration – Japan works with other countries including India to promote advancement and share knowledge.
India
- Govt. initiatives – The Nano Mission was started by India’s Department of Science and Technology in 2007. Its goal was to build a strong base in nanoscience and nanotechnology. The main goal of this program is to do research, development, and marketing of nanotechnology products.
- Research and Development – The Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) and the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) are two of the best places to study nanotechnology. For example, scientists from IISER Pune and IIT Bombay came up with a way to make metal nanoparticles that are all the same size, which makes it easier to find diseases and keep an eye on the environment.
- Industry applications – Nanotechnology is used in healthcare, agriculture, and energy. At Banaras Hindu University, Curcumin Quantum Dots (CurQDs) improve the solubility and bioavailability of compounds for pharmaceutical applications. a remarkable example of how What Is Nanotechnology is advancing modern science and medicine.
Indonesia
- Research and development – Indonesia has been developing nanotechnology since 2004. It has produced nanotechnology-based products in agriculture, food, textiles, automotive, and healthcare.
- Infrastructure – The creation of the Nano Device Laboratory at Universitas Indonesia is an important step toward improving nanotechnology research and development in the country. It highlights how What Is Nanotechnology is fostering innovation and strengthening scientific capabilities across the region.
- Opportunities – Emerging economies can use nanotechnology to tackle local issues in healthcare, agriculture, and energy. For example, nanotechnology can help create affordable diagnostic tools, increase crop yields, and boost energy efficiency.
- Challenges – These economies encounter obstacles like limited research facilities, a shortage of skilled workers, and the need for policies to support nanotechnology innovation.

ECONOMIC , INDUSTRIAL AND SOCIAL EFFECT OF NANOTECHNOLOGY
- Economic effect – Nanotechnology improves GDP and employment by promoting innovative tech sectors and creating jobs in manufacturing, services, and research. It opens new markets in coatings, sensors, drug delivery, and high-quality materials — turning industries such as packaging, textiles, and cosmetics into multibillion-dollar sectors, demonstrating how What Is Nanotechnology drives economic growth and industrial transformation. Nanotechnology is fueling a massive shift in global economics, moving us away from resource-heavy industries to knowledge-based high-value manufacturing.
- GDP & Employment: What Is Nanotechnology doing for the economy? It is projected to be a multi-trillion-dollar industry by 2030. It creates high-skilled jobs not just in labs, but in manufacturing hubs producing next-gen chips, batteries, and medical devices.
- New Markets & Value Chains:
- Smart Packaging: Antimicrobial nano-coatings on food packaging extend shelf life, saving billions in food waste annually.
- Cost Efficiency: Nanomaterials often require less raw mass to achieve superior strength or conductivity. For example, using Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) in construction reduces the volume of concrete needed, slashing both costs and transport logistics.
- Intellectual Property: A race for “Nano-Patents” is currently underway between major economies (USA, China, EU), signaling that ownership of nanoscale innovations will define future economic dominance.
- Industrial Impact – Nanotechnology is transforming manufacturing, allowing the aerospace, automotive, and construction industries to develop stronger, lighter, and more strong materials, like carbon nanotube-reinforced items . It drives high quality electronics with smaller, faster, and more power-efficient systems, enhancing memory, sensors, and semiconductors. Nanotechnology is transforming manufacturing, allowing the aerospace, automotive, and construction industries to develop materials that were previously impossible to create.
- Aerospace & Automotive:
- Lighter & Stronger: By replacing steel with carbon nanotube-reinforced composites, manufacturers can reduce the weight of aircraft and electric vehicles (EVs). A lighter plane burns less fuel; a lighter EV has a longer range.
- Electronics & Computing:
- Moore’s Law & Beyond: As silicon chips reach their physical limits, What Is Nanotechnology steps in. New 2nm (nanometer) transistor nodes allow for faster, cooler, and more power-efficient smartphones and servers.
- Energy Sector Revolution:
- Social Impact – Nanotechnology improves healthcare by enhancing diagnostics, drug delivery, and regenerative medicine while reducing costs. It also promotes environmental sustainability through waste management, pollution control, and water purification — showing how What Is Nanotechnology contributes to both human well-being and a cleaner planet. The social impact of What Is Nanotechnology is perhaps the most profound, as it directly affects human health, safety, and the environment.
- Healthcare (Nanomedicine):
- Targeted Delivery: Nanoparticles act as “molecular taxis,” delivering chemotherapy drugs directly to cancer cells while ignoring healthy ones. This drastically reduces side effects and costs.
- Rapid Diagnostics: During the COVID-19 pandemic, nanotechnology (via Lipid Nanoparticles) was the unsung hero that made mRNA vaccines stable and effective.
Ethical, Environmental, and Health Consideration

Ethical considerations
- Accessibility and Equity : Nanotechnology may widen the gap between developed and developing nations. If high-tech medicines, energy systems, and products remain costly, only wealthier nations and populations will benefit. a concern that highlights the need for fair access and global inclusion in the progress of What Is Nanotechnology.
- Privacy and Security : Nanosensors and surveillance tools cause worries regarding data privacy, tracking and misuse by govt. and corporations.
- Human Enhancement : Utilization of nano- medicine and nano- implants may rise to ethical discussions regarding human improvement and natural biological boundaries .
- Dual-Use Risk : Nanotech innovations could also be used for harmful purposes, such as military nanoweapons or toxic nanomaterials, raising serious concerns about responsible governance and ethical use — an important issue within the scope of What Is Nanotechnology.
Environmental Considerations
- Nanoparticle Release : Throughout production , use and removal nanoparticles can enter sand , water and air impacting ecosystems.
- Positive Environmental Role : However , nanotechnology supports ecofriendly innovations such as water purification, renewable energy and pollution control managing its risks.
Health Considerations
Nanotechnology’s unique scale requires strict health risk research, especially regarding inhalation toxicity.
- Size & Reactivity: Nanoparticles ($< 100 \text{ nm}$) bypass biological defenses and their high surface area increases reactivity, potentially causing cellular oxidative stress.
- Carbon Nanotube (CNT) Risk: Long, fibrous CNTs are a major concern. In animal studies, inhaled CNTs have caused pulmonary inflammation similar to asbestos, with the potential to translocate from the lungs to other organs.
- Regulatory Gap: Developing safe Occupational Exposure Limits (OELs) is challenging, as the high diversity of new nanomaterials requires continuous, specific safety assessments.
Public Considerations
- Trust and transparency : Absence of public awareness can result in fear and opposition similar to debates around GMOs. Effective communication regarding benefits and risks is important.
- Ethical marketing : Firms should avoid overstating the benefits of nanotechnology and hide potential risks.
- Social acceptance : Extensive use will rely on people’s confidence in regulations and safety measurements.
FUTURE TRENDS AND EMERGING FRONTIERS
Nanorobotics
robots at the nanoscale which can carry the operations at the molecular or cellular level.
- Applications – It can be used in drug delivery, precision surgery, cleaning pollutants , assembling nanoscale particles in manufacturing.
- Future trends – Creating autonomous, self repairing nanorobots integrated with AI for use in medicine and manufacturing .
Nanoelectronics
Electronics employ nanomaterials and nanoscale systems to obtain high performance.
- Applications – It can be used in memory storage and ultra high processors , widely sensitive environmental sensors and reducing energy consumption while improving power .
- Future trends – Combining with quantum computing and neuromorphic devices to enable ultra- efficient power computing and AI acceleration.
Nanomedicine
It can be used in healthcare for diagnosis, treatment and monitoring.
- Future trends – Customized nanomedicine employing AI and biosensors for monitoring patient’s health.
Quantum Nanotechnology
Controlling matter at the atomic and subatomic scale to harness quantum phenomena.
- Applications – It can be used in qubits for widely superior computation, so precise measurements of time, gravity and magnetic system.
- Future trend – leveling quantum systems for their commercial use, incorporation with nanomaterials to develop hybrid quantum-nano systems.
Overall Emerging Trend
- The central themes across all these domains are combining of AI, robotics and quantum rules with nanotech allowing ultra precise high performance and solutions in medicines, electronics, environmental management and space exploration. Ethical guidelines and safety rules will be important as these technologies advance.
Conclusion
Nanotechnology is redefining the limits of the entire science and helping to create Unique Business Ideas that focus on developing smarter, stronger, and more sustainable designs by working at the atomic and molecular level. Understanding what is nanotechnology helps explain how it has driven innovation in healthcare, energy, electronics, and the environment through solar panels, borderless targeted drugs, and lightweight materials.
Combined with Artificial Intelligence, they are faster, more accurate, and cost-effective in discoveries. Shark Mondo, a digital marketing agency, often highlights how emerging technologies like nanotech are reshaping industries and inspiring innovative solutions. Nevertheless, the ethics, safety, and sensitization of people should ensure that this mighty technology is put into a sound direction. With fresh impetus in the development of nanotech, the technology remains a major influencer of the future of innovation, sustainability, and human development.

