Table of Contents
what are the three goals of cybersecurity
INTRODUCTION

What are the three goals of cybersecurity? Confidentiality means sensitive information is only accessible to those who are allowed. Integrity means data can’t be altered, manipulated, or corrupted and remains accurate and reliable. Availability means information and resources are available when needed, with minimal disruption. In a digital world where businesses, governments, and individuals rely so heavily on technology, cybersecurity is more important than anything other than that.
Cybersecurity is the practice of defending systems, networks, and data from attacks, unauthorized access, and harm. At the heart of cybersecurity are three main goals, commonly known as the CIA Triad—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. These three goals together answer the question, “what are the three goals of cybersecurity?” Together, they form the basis of every cybersecurity strategy. They protect digital assets, build trust, and support operations and resilience against ever-changing cyber threats. Now, let’s read more about these three major goals in detail.
WHAT IS CYBERSECURITY?

Cybersecurity refers to the collection of techniques, processes, tools, and actions used to protect computer systems, networks, and data from cyber attacks and unauthorized access. It also focuses on understanding what are the three goals of cybersecurity—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—to build a strong defense framework. Its base is in technology, but at the end of the day, people are crucial to making security work.
In some cases, human mistakes or carelessness create possible attack vectors that are easy for cybercriminals to exploit. When people understand what are the three goals of cybersecurity and take the time to implement best practices, know their facts, and apply proper security measures, the chances of breaches can be greatly reduced, helping computer systems remain secure.
WHY DO WE NEED CYBERSECURITY?

Cybersecurity is significant because it applies to all types of data that have been categorized. This includes sensitive data, protected health information (PHI), personal information, intellectual property, data, personally identifiable information (PII), and governmental and industry information systems. Understanding what are the three goals of cybersecurity—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—helps in protecting these valuable assets effectively. Without a strong cybersecurity program, your organization will be unable to defend itself against data breach campaigns, offering cybercriminals an opportunity they simply cannot refuse.
The inherent risk and the residual risk are both on the rise due to global connectivity and the use of cloud services, such as Amazon Web Services, to store sensitive data and personal information. Understanding what are the three goals of cybersecurity—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—has become essential in addressing these risks effectively. Growing pressures mean it’s more likely than ever that your organization could be seriously compromised by a high-impact cyberattack or data breach, as misconfigured cloud services continue to reach unprecedented levels and cybercriminals modernize their approaches.
Generic cybersecurity tools like antivirus software and firewalls aren’t good enough anymore—cybercriminals are getting smarter, and their attacks are becoming harder to counter with off-the-shelf solutions. Understanding what are the three goals of cybersecurity—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—helps highlight why organizations must strengthen their defenses beyond basic tools.
The necessity to be prepared on all fronts of cybersecurity is vital. Understanding what are the three goals of cybersecurity—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—helps organizations and individuals build stronger digital defenses. As digital transformation accelerates, it has completely changed the way businesses operate and people shop, work, and communicate, with e-commerce, remote collaboration, and cloud data storage becoming staples of modern life.
In addition to individual and corporate use, essential networks such as gas pipelines, electrical grids, and other vital services are now managed through the internet, making them increasingly susceptible to cyberattacks. Understanding what are the three goals of cybersecurity—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—helps emphasize why protecting these systems is so critical. As organizations and consumers continue placing more sensitive information on digital platforms, the importance of effective cybersecurity measures has never been higher. These measures not only secure valuable information but also maintain the stability and integrity of services that impact millions of lives every single day.
3 MAJOR GOALS OF CYBERSECURITY
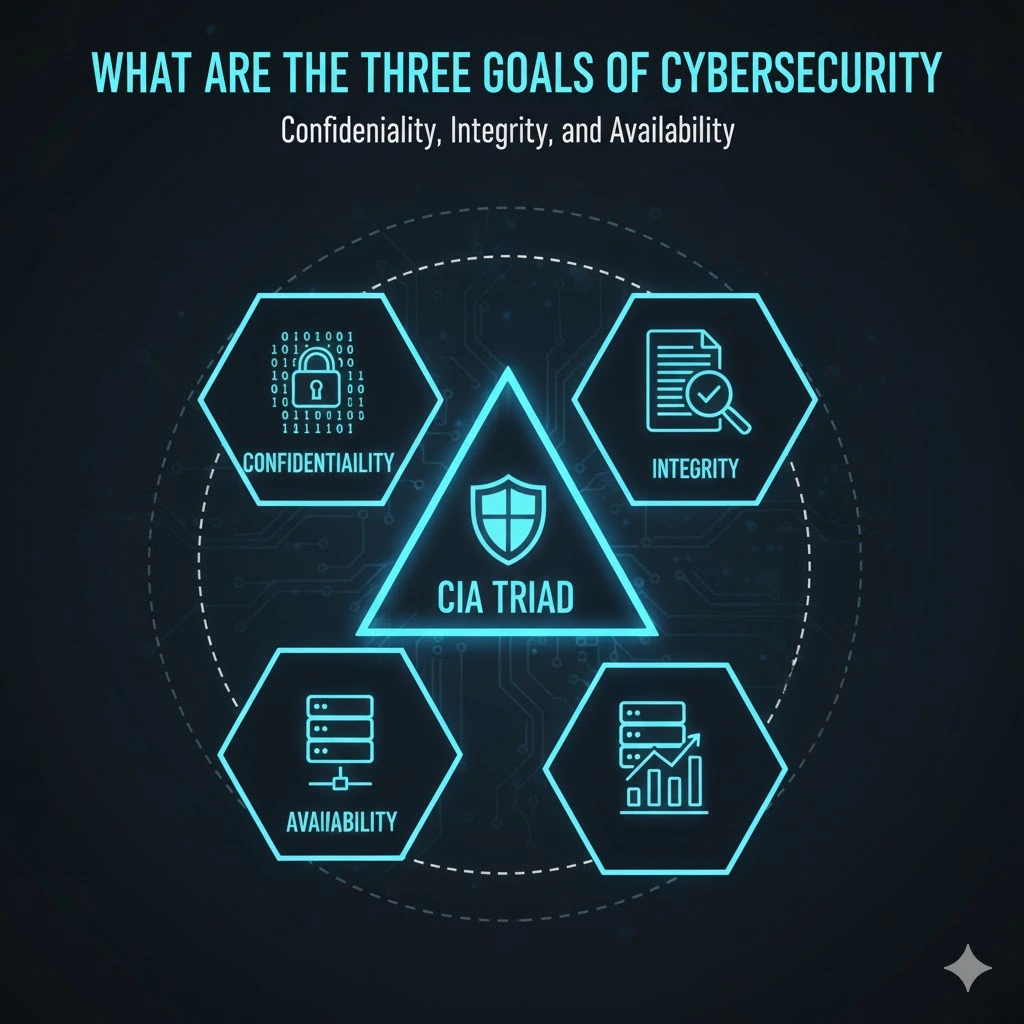
In cybersecurity, there is a foundational model called the CIA Triad, which identifies the three primary goals of security.
What are the three goals of cybersecurity : 1.Confidentiality, 2.Integrity, 3.Availability
Together, they provide a framework for designing, evaluating, and operating secure systems.
1. Confidentiality
Confidentiality means ensuring that sensitive information is accessible only to those who are authorized to see it, and preventing unauthorized disclosure.
It’s about privacy and controlling what data is exposed, to whom, and under what conditions.
Threats / Risks
Some common ways confidentiality is threatened include:
- Unauthorized access (e.g. hacking, credential theft)
- Eavesdropping or interception in transit (man-in-the-middle attacks)
- Insider threat (employees or insiders misusing privileges)
- Improper data handling (e.g. leaving sensitive files exposed)
- Social engineering (phishing, deception)
Typical Controls / Measures
To enforce confidentiality, organizations use:
- Access control systems (role-based access, least privilege)
- Strong authentication (multi-factor authentication)
- Encryption (data at rest, data in transit)
- Secure communication channels (VPN, TLS/SSL)
- Data classification, labeling, and policies
- Physical security (locking servers, restricting physical access)
2. Integrity
Integrity means ensuring that data is accurate, complete, and believable . It ensures the trustworthiness and reliability of information over its entire lifecycle (creation, storage, transmission, retrieval).
Threats / Risks
Integrity can be compromised via:
- Unauthorized modification (tampering)
- Data corruption (hardware failures, software bugs)
- Replay attacks, injection attacks, or malicious data input
- Insider alteration or fraud
- Inadvertent changes or errors
Typical Controls / Measures
To protect integrity, security strategies include:
- Checksums, hashes, and cryptographic hashing
- Digital signatures
- Versioning and audit logs
- Input validation and sanitization
- Access controls and separation of duties
- Intrusion detection and integrity monitoring tools
- Secure backups (with integrity checks)
3. Availability
Availability means that authorized users are able to access the systems and data when needed, without delay or interruption.
Threats / Risks
Availability can be threatened by:
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) or Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks
- Hardware failures (disk crashes, power outages)
- Natural disasters or catastrophes
- Network outages or congestion
- Malware, ransomware or destructive attacks
- Overloads, insufficient capacity
Typical Controls / Measures
To ensure availability, organizations use:
- Redundancy (multiple systems, failover)
- Load balancing, clustering
- Backup and disaster recovery planning
- Continuity planning and recovery drills
- Capacity planning and monitoring
- High-availability architectures
- Patch management (to avoid downtime)
# Confidentiality VS Availability VS Integrity
These three goals are not independent—they often have tensions:
- Balancing confidentiality vs. availability : Tighter access controls or strong encryption may slow performance or complicate access, potentially reducing availability.
- Integrity vs. availability : Strict integrity checks might delay or reject changes (i.e. deny legitimate updates) if they appear suspicious.
- In practice, security solutions—such as policies, tools, and architecture—are designed to balance all three goals, known as what are the three goals of cybersecurity: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. These goals are aligned in a way that suits the organization’s risk tolerance and operational requirements.
REAL WORLD APPLICATIONS OF CIA TRIAD
1. Banking and Finance Confidentiality
- To keep information about clients (passwords and account numbers) safe from hackers, banks gets secure login and encryption.
- Integrity : Transaction logs and audit leads to prevent unauthorized changes to financial records or accounts.
- Availability : You can access online banking and ATMs around-the-clock thanks to secure systems and backup servers.
2. Healthcare Confidentiality
- Secure hospital databases and limited access are used to safeguard patient records according to data privacy rules(such as HIPAA).
- Integrity : Prescriptions and medical reports must be accurate; any deviation could lead to incorrect treatment. Understanding what are the three goals of cybersecurity—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—is vital in such cases. Digital signatures are used by hospitals to guard against fraud and ensure the integrity of medical data.
- Availability : Systems must have safe cloud backups and power redundancies because physicians and staff require round-the-clock access to patient data.
3. E-Commerce Confidentiality
- HTTPS and SSL are used by websites to safeguard consumer payment information when they make payments online.
- Integrity : Order information, customer reviews, and product prices are protected from hackers.
- Availability : To remain online even in the event of cyberattacks, e-commerce websites such as Amazon and Flipkart employ load balancers and backup servers. This approach reflects what are the three goals of cybersecurity—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—by ensuring that their platforms stay accessible and reliable for users at all times.
4. Government and Defense Confidentiality:
- HTTPS and SSL are used by websites to safeguard consumer payment information when they make purchases online.
- Integrity : Order information, customer reviews, and product prices are protected from hackers.
- Availability : To remain online even in the event of high traffic or cyberattacks, e-commerce websites such as Amazon and Flipkart employ load balancers and backup servers. This demonstrates what are the three goals of cybersecurity—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—by maintaining smooth operations, protecting data, and ensuring uninterrupted access for users.
5. Education Confidentiality
- Personal information, grades, and student records are kept in secure databases with limited access.
- Integrity : To avoid illegal grade adjustments or attendance data manipulation, universities employ secure systems.
- Availability : Students and staff must have uninterrupted access to learning management systems (such as Google Classroom or Moodle).
6. Cloud Computing Confidentiality:
- Ensuring uploaded files remain unchanged through data validation and routine integrity checks.
- Availability : You’re up even during outages thanks to the multiple data centers of cloud platforms like Microsoft Azure and Google Drive
BASIC PRECAUTIONS TOWARDS OUR VIRTUAL SAFETY
In this contemporary digital age, the internet has attained a vital position in our day-to-day life. We use it for communication, learning, shopping, banking, and entertainment. But with technology comes an increase in vulnerabilities such as hacking, phishing, and identity theft. Understanding what are the three goals of cybersecurity—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—helps us recognize the importance of online protection. To save ourselves from these perils, it is extremely important to follow some simple safety tips in the virtual space.
1. Use Strong Passwords
Always provide strong, guess-proof passwords by pairing uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid using simple words. Understanding what are the three goals of cybersecurity—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—reminds us that even a password plays a key role in protecting data and maintaining system integrity. A personal password should not be simple or easy to figure out and should include alphanumeric characters and special symbols, such as “J0hn#89Secure”.Secure”.
2. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication adds another verification step, such as an OTP or security code, helping secure your account even if someone knows the password. This practice supports what are the three goals of cybersecurity—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—by ensuring that only the rightful user can access the account.
3. Be Cautious with Links and Attachments
Do not click on unknown or suspicious links included in emails, messaging apps, or social media posts; they may contain malware or viruses that can steal your private information. Understanding what are the three goals of cybersecurity—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—helps emphasize why such caution is necessary. Always verify the identity of the sender before clicking any link or sharing personal details.
4. Keep Software and Devices Updated
Always update your mobile, computer, and software regularly. Every update comes with new security features and bug fixes that strengthen protection. Understanding what are the three goals of cybersecurity—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—highlights why timely updates are so essential. These updates protect computers from hackers’ new tricks, while outdated software becomes more vulnerable to viruses. Therefore, it is very important to update the operating system, apps, and antivirus from time to time.
5. Stay Alert on Social Media
Always be careful with what you share on social platforms. For example, do not post your personal details, address, school or college name, or your current location. Cybercriminals can misuse such information. Understanding what are the three goals of cybersecurity—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—reminds us how important it is to protect personal data online. Avoid posting anything that could help someone commit identity theft or create fake accounts, and choose to share your details publicly only with trusted people.
6. Avoid Using Public Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi networks in public places like malls, cafes, or railway stations are not safe because hackers can easily steal data through such connections. Understanding what are the three goals of cybersecurity—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—helps explain why using public Wi-Fi without protection is risky. Never make online payments, access banking services, or enter login passwords on such networks. If you must use them, always connect through a VPN (Virtual Private Network) to keep your connection secure and safe.
7. Backup Important Data
Always make sure to back up your important documents, files, and photos to cloud storage like Google Drive, OneDrive, or external hard drives. Understanding what are the three goals of cybersecurity—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—highlights why regular backups are essential for maintaining data availability and safety. If your phone or computer is ever hacked or data is deleted, you can easily restore it. Backing up is a smart and secure practice. Also, keep yourself informed and aware.
8. Stay Informed and Aware
Cyberattacks are a growing issue, which is why it is of great importance to stay informed. We must familiarize ourselves with the latest scams, phishing methods, and online safety tips. Understanding what are the three goals of cybersecurity—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—forms the foundation of this awareness and helps us recognize potential threats before encountering them. In short, when you are aware of the dangers, you are better equipped to avoid them.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, all digital security measures are built upon what are the three goals of cybersecurity—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—also known as the “CIA Triad.” These goals ensure that data remains accurate, private, and available to authorized users at all times.
Keeping these three objectives in balance is crucial for protecting data, systems, and user trust in the current digital era, where cyber threats are growing quickly. In the same way, using the right Digital Marketing Tools also plays a vital role in ensuring secure and efficient online operations while maintaining data integrity and trust.
People and organizations can create a secure digital environment that facilitates safe communication, business continuity, and general technological advancement by comprehending and successfully implementing the CIA triad. Shark Mondo, a digital marketing agency, also emphasizes the importance of cybersecurity principles like the CIA triad to ensure data protection and maintain trust in the digital world.